What is Crohn’s Disease?
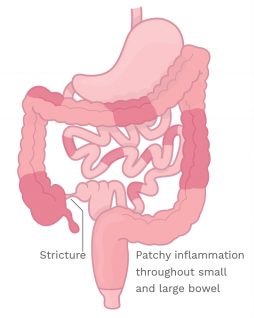
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory condition that can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall or any part of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes leaving patches of diseased intestine among the normal areas. It can disrupt your body’s ability to digest food, absorb nutrition, and eliminate waste in a healthy manner. Over time, it also poses an increased risk for one to develop blood clots or colon cancer.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms can vary from person to person, depending on the type of Crohn’s disease and complication.
Common GI symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Bowel urgency
- Diarrhea
- Blood in the stool
Those with severe Crohn’s disease may also experience symptoms outside of the intestinal tract, including:
- Inflammation of skin, eyes, and joints
- Inflammation of the liver or bile ducts
- Kidney stones
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Delayed growth or sexual development (in children)
Over time, Crohn’s can lead to further complications such as:
- Bowel obstruction
- Ulcers
- Fistulas
- Anal fissures
- Malnutrition
Why do people develop Crohn’s disease?
There are several factors that can contribute to the development this condition, including:
- An Autoimmune Reaction: Your immune system can attack healthy cells in your body. Experts believe that bacteria in your digestive tract can mistakenly trigger your immune system, which causes inflammation leading to symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
- Genes: Crohn’s disease sometimes runs in families. Research has shown that if you have a parent or sibling with Crohn’s disease, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
- Smoking: Smoking doubles your risk of developing Crohn’s disease. Research also suggests that smoking can make Crohn’s worse. Studies show that smokers often have more severe symptoms and complications from Crohn’s disease than non-smokers.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Aspirin, ibuprofen, antibiotics, and birth control pills may slightly increase the chance of developing Crohn’s disease.
- High Fat Diet: Eating fatty foods and a diet rich in high-fat items may slightly increase your chances of developing Crohn’s disease.
Is there a cure?
There is no known cure for Crohn’s disease. Even so, lifestyle changes along with several treatment options are available that can greatly reduce symptoms and even bring about long-term remission and healing of inflammation.
Think you may have Crohn’s disease?
Please see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.

