Services
HOW WE CAN HELP YOU
Services & Procedures

Colonoscopy
An endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected colorectal cancer lesions.
Capsule Endoscopy
A capsule endoscopy uses a pill sized video camera that you swallow to allow examination of the small intestine. This camera continuously takes pictures as it passes through your digestive tract, saving them to a small recording device for later evaluation.
Endoscopy
Allows the physician to see the upper GI tract including the esophagus, stomach and the duodenum using an endoscope. It evaluates difficulty swallowing, upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, can detect inflammation, ulcers, or tumors in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum.
Endoscopic Ultrasound
An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a test performed that allows your doctor to examine the lining and the walls of your upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, or to study closeby internal organs such as the gallbladder and pancreas.
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a short procedure typically done without sedation that allows the doctor to examine the lining of the rectum and lower part of the colon by inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the anus.
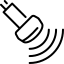
FibroScan Liver Test
FibroScan is a tool used for non-invasive examinations of the liver. It works by releasing a small pulse of energy to calculate the speed of energy as it travels through your liver, allowing for interpretation of the liver’s stiffness and fat.

Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT)
Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT) is a therapy for those with recurrent and severe clostridium difficile infection (C-diff). C-diff is a bacteria that is present in the intestine of some individuals, and its problems can range from a mild illness with diarrhea to a severe life-threatening condition requiring hospitalization.

Hemorrhoid Banding
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum that may cause discomfort. There are two types: external or internal. External hemorrhoids tend to be painful, whereas internal hemorrhoids tend to cause symptoms such as: itching, bleeding, swelling, prolapse, and/or leakage.

Interstim Bowel Control Therapy
InterStim Therapy helps treat chronic fecal incontinence by restoring communication between the brain and bowel through gentle nerve stimulation. If other treatments haven’t worked, this therapy may provide lasting relief. GAP offers evaluations and trial procedures to determine if you’re a candidate.
